Little Kit's Coty House
 The stones of Little Kit's Coty House as they now appear | |
 | |
| Alternative name | Lower Kit's Coty House |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 51°18′57″N 0°30′05″E / 51.3159675°N 0.5013867°E |
| Type | Long barrow |
| History | |
| Periods | Early Neolithic |
Little Kit's Coty House, also known as Lower Kit's Coty House and the Countless Stones, is a chambered long barrow located near to the village of Aylesford in the southeastern English county of Kent. Constructed circa 4000 BCE, during the Early Neolithic period of British prehistory, today it survives in a ruined state.
Archaeologists have established that the monument was built by pastoralist communities shortly after the introduction of agriculture to Britain from continental Europe. Although representing part of an architectural tradition of long barrow building that was widespread across Neolithic Europe, Kit's Coty House belongs to a localised regional variant of barrows produced in the vicinity of the River Medway, now known as the Medway Megaliths. Of these, it lies near to both Kit's Coty House and the Coffin Stone on the eastern side of the river. Three further surviving long barrows, Addington Long Barrow, Chestnuts Long Barrow, and Coldrum Long Barrow, are located west of the Medway.
Now a jumble of half-buried sarsen stones it is thought to have been a tomb similar to that of the Coldrum Stones. The name is derived from the belief that the chaotic pile of stones from the collapsed tomb were uncountable and various stories are told about the fate of those who tried. Another nearby site that may have been Neolithic is at Cossington. There are between 19 and 21 stones depending on the authority. They were pushed over in the seventeenth century seemingly before any antiquarian interest was taken in them. William Stukeley attempted to reconstruct the damaged tomb in plan in the eighteenth century.
Archaeological evaluation trenching in 1989 found no clear evidence of any surrounding quarry ditch which would normally have been excavated to provide material for a covering barrow.
Name and location
[edit]Little Kit's Coty House is also known as Lower Kits Coty,[1] and as the Countless Stones.[2] The site is enclosed in iron railings and permanently open to visitors.[3] It is approximately 460 metres (500 yd) south of another of the Medway Megaliths, Kit's Coty House.[1] It is about 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) northeast of Aylesford, and is signposted from the Rochester Road.[3]
Context
[edit]The Early Neolithic was a revolutionary period of British history. Between 4500 and 3800 BCE, it saw a widespread change in lifestyle as the communities living in the British Isles adopted agriculture as their primary form of subsistence, abandoning the hunter-gatherer lifestyle that had characterised the preceding Mesolithic period.[4] This came about through contact with continental European societies, although it is unclear to what extent this can be attributed to an influx of migrants or to indigenous Mesolithic Britons adopting agricultural technologies from the continent.[5] The region of modern Kent would have been key for the arrival of continental European settlers and visitors, because of its position on the estuary of the River Thames and its proximity to the continent.[6]
Britain was then largely forested;[7] widespread forest clearance did not occur in Kent until the Late Bronze Age (c.1000 to 700 BCE).[8] Environmental data from the vicinity of the White Horse Stone, a putatively prehistoric monolith near the River Medway, supports the idea that the area was still largely forested in the Early Neolithic, covered by a woodland of oak, ash, hazel/alder and amygdaloideae.[9] Throughout most of Britain, there is little evidence of cereal or permanent dwellings from this period, leading archaeologists to believe that the island's Early Neolithic economy was largely pastoral, relying on herding cattle, with people living a nomadic or semi-nomadic life.[10]
Medway Megaliths
[edit]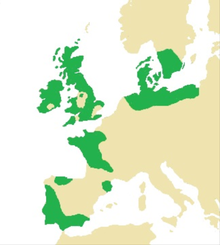
Across Western Europe, the Early Neolithic marked the first period in which humans built monumental structures in the landscape.[11] These structures included chambered long barrows, rectangular or oval earthen tumuli which had a chamber built into one end. Some of these chambers were constructed out of timber, although others were built using large stones, now known as "megaliths".[12] These long barrows often served as tombs, housing the physical remains of the dead within their chamber.[13] Individuals were rarely buried alone in the Early Neolithic, instead being interred in collective burials with other members of their community.[14] These chambered tombs were built all along the Western European seaboard during the Early Neolithic, from southeastern Spain up to southern Sweden, taking in most of the British Isles;[15] the architectural tradition was introduced to Britain from continental Europe in the first half of the fourth millennium BCE.[16] Although there are stone buildings—like Göbekli Tepe in modern Turkey—which predate them, the chambered long barrows constitute humanity's first widespread tradition of construction using stone.[17]
Although now all in a ruinous state and not retaining their original appearance,[18] at the time of construction the Medway Megaliths would have been some of the largest and most visually imposing Early Neolithic funerary monuments in Britain.[19] Grouped along the River Medway as it cuts through the North Downs,[20] they constitute the most southeasterly group of megalithic monuments in the British Isles,[21] and the only megalithic group in eastern England.[22] The archaeologists Brian Philp and Mike Dutto deemed the Medway Megaliths to be "some of the most interesting and well known" archaeological sites in Kent,[23] while the archaeologist Paul Ashbee described them as "the most grandiose and impressive structures of their kind in southern England".[24]
The Medway Megaliths can be divided into two separate clusters: one to the west of the River Medway and the other on Blue Bell Hill to the east, with the distance between the two clusters measuring at between 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) and 10 kilometres (6.2 mi).[25] The western group includes Coldrum Long Barrow, Addington Long Barrow, and the Chestnuts Long Barrow.[26] The eastern group consists of Smythe's Megalith, Kit's Coty House, and Little Kit's Coty House, while various stones on the eastern side of the river, most notably the Coffin Stone and White Horse Stone, may also have been parts of such structures.[27] It is not known if they were all built at the same time, or whether they were constructed in succession,[28] while similarly it is not known if they each served the same function or whether there was a hierarchy in their usage.[29]

The Medway long barrows all conformed to the same general design plan,[30] and are all aligned on an east to west axis.[30] Each had a stone chamber at the eastern end of the mound, and they each probably had a stone facade flanking the entrance.[30] They had internal heights of up to 3.0 metres (10 feet), making them taller than most other chambered long barrows in Britain.[31] The chambers were constructed from sarsen, a dense, hard, and durable stone that occurs naturally throughout Kent, having formed out of sand from the Eocene epoch.[32] Early Neolithic builders would have selected blocks from the local area, and then transported them to the site of the monument to be erected.[32]
These common architectural features among the Medway Megaliths indicate a strong regional cohesion with no direct parallels elsewhere in the British Isles.[33] Nevertheless, as with other regional groupings of Early Neolithic long barrows—such as the Cotswold-Severn group in south-western Britain—there are also various idiosyncrasies in the different monuments, such as Coldrum's rectilinear shape, the Chestnut Long Barrow's facade, and the long, thin mounds at Addington and Kit's Coty.[34] These variations might have been caused by the tombs being altered and adapted over the course of their use; in this scenario, the monuments would be composite structures.[35]
The people who built these monuments were probably influenced by pre-existing tomb-shrines that they were already aware of.[36] Whether those people had grown up locally, or moved into the Medway area from elsewhere is not known.[36] Based on a stylistic analysis of their architectural designs, the archaeologist Stuart Piggott thought that the plan behind the Medway Megaliths had originated in the area around the Low Countries,[37] while fellow archaeologist Glyn Daniel instead believed that the same evidence showed an influence from Scandinavia.[38] John H. Evans instead suggested an origin in Germany,[39] and Ronald F. Jessup thought that their origins could be seen in the Cotswold-Severn megalithic group.[40] Ashbee noted that their close clustering in the same area was reminiscent of the megalithic tomb-shrine traditions of continental Northern Europe,[24] and emphasised that the Medway Megaliths were a regional manifestation of a tradition widespread across Early Neolithic Europe.[41] He nevertheless stressed that a precise place of origin was "impossible to indicate" with the available evidence.[42]
Design and construction
[edit]
In 2005, Philp and Dutto noted that there were about 21 stones at the site.[3] Jessup called it a "confused group",[1] while the archaeologist Timothy Champion termed it "a jumble".[30] Many of these would have once formed part of a chamber at the eastern end of a long, rectangular earthen mound.[30] Philp and Dutto believed that some of the stones were from the long barrow's chamber and others from its façade, adding that it was "just possible" to suggest which is which.[3]
The sarsens found at Little Kit's Coty House are among the largest known from the Medway Megaliths.[30] Using their measurements as a basis, Ashbee proposed that the chamber would have been 5.2 metres (17 ft) long, 2.4 metres (8 ft) wide, and 2.7 metres (9 ft) high.[43] He suggested that, when the monument was viewed from the east, it became clear that the stones had fallen to the north from their original positions.[44] He believed that if the site were fully excavated, the holes in which the sarsen stones originally stood could might be identified, allowing for the chamber to be reconstructed in a manner similar to that at Chestnuts Long Barrow.[43]
Jessup believed that it was "impossible to trace the form of the original structure".[1] Ashbee thought it might have once been "one of the more massive" of the Medway Megaliths,[45] with Champion concurring, suggesting that the long barrow would have been at least 20 metres (66 ft) in width and possibly over 90 metres (300 ft) in length.[30] The mound may have been encircled by a ditch, since filled in by hillwash.[43]
Meaning and purpose
[edit]Britain's Early Neolithic communities placed greater emphasis on the ritual burial of the dead than their Mesolithic forebears.[14] Archaeologists have suggested that this is because Early Neolithic Britons adhered to an ancestor cult that venerated the spirits of the dead, believing that they could intercede with the forces of nature for the benefit of their living descendants.[46] The archaeologist Robin Holgate stressed that rather than simply being tombs, the Medway Megaliths were "communal monuments fulfilling a social function for the communities who built and used them".[28] Thus, it has been suggested that Early Neolithic people entered into the tombs—which doubled as temples or shrines—to perform rituals honouring the dead and requesting their assistance.[47] For this reason, the historian Ronald Hutton termed these monuments "tomb-shrines" to reflect their dual purpose.[17]
In Britain, these tombs were typically located on prominent hills and slopes overlooking the landscape, perhaps at the junction between different territories.[48] The archaeologist Caroline Malone noted that the tombs would have served as one of various landscape markers that conveyed information on "territory, political allegiance, ownership, and ancestors".[49] Many archaeologists have subscribed to the idea that these tomb-shrines were territorial markers between different tribes; others have argued that such markers would be of little use to a nomadic herding society.[50] Instead it has been suggested that they represent markers along herding pathways.[51] The archaeologist Richard Bradley suggested that the construction of these monuments reflects an attempt to mark control and ownership over the land, thus reflecting a change in mindset brought about by the transition from the hunter-gatherer Mesolithic to the pastoralist Early Neolithic.[52] Others have suggested that these monuments were built on sites already deemed sacred by Mesolithic hunter-gatherers.[53]
Damage and dilapidation
[edit]All the surviving megalithic tombs from the Early Neolithic period have suffered from neglect and the ravages of agriculture.[54] Little Kit's Coty House has been damaged on more than one occasion.[1] In 1773, Douglas was told that a farmer had dismantled the monument to use its stones for road metal but that the stones proved too large for this purpose.[1]
Folklore, folk tradition, and modern Paganism
[edit]
In 1722, the antiquarian Hercules Ayleway noted—in a letter written to his friend, the fellow antiquarian William Stukeley—a local belief that the Lower Kit's Coty House and Kit's Coty House were erected in memory of two contending kings of Kent who died in battle.[55]
The archaeologist and folklorist Leslie Grinsell believed that the countless stones motif would only have been applied to the site after the chamber had been toppled, something he suggested had occurred around 1690.[56] Grinsell noted that as of the mid-twentieth century, that folklore was still extant, citing the discovery of numbers written in chalk on the different stones.[56]
Several modern Pagan religions are practised at the Medway Megaliths, the most publicly visible of which is Druidry.[57] Research conducted among these Druids in 2014 revealed that some Druidic activity had taken place at Little Kit's Coty House but that at least one Druid disliked performing rituals there because of the noise produced by nearby power cables.[57]
Antiquarian and archaeological investigation
[edit]
The antiquarian John Aubrey referenced a range of prehistoric sites across Britain in his manuscript, Monumenta Britannica, written over the course of 1663 to 1693. In this manuscript, he quoted from a letter sent to him by Dr Thomas Gale, the Master of St Paul's School in London. In the letter, Gale reported that "In the field next to this [Kit's Coty House] nearer to Ailsford, are 13 or 14 great stones; seven standing, all covered with one large stone, the rest are fallen down. The people call this also Kit's Coty-house."[58] Aubrey's book was not published until several centuries later, and it is possible that the site was further damaged in the years following Gale's letter.[58]
The antiquarian William Stukeley visited the area in 1722.[58] At this point the stones had already been pulled down; from a letter sent to him that year by Hercules Ayleway it appears that the chamber was dismantled around thirty years prior.[59] Ayleway had written that "I have been informed by some who remember it standing that the stones which composed the wall did all of them joyn [sic] close together so as to touch each other, and the dore [sic] was on the west side thereof, next the road."[60] Stukeley produced several illustrations of the site, which were published posthumously.[59] One, produced in October 1722 and used as the basis for a public plate, includes Little Kit's Coty House as a cove in the foreground, while Kit's Coty House — including its barrow — can be seen in the background.[61] However, his depiction of the monument differs in these two illustrations, rendering their accuracy unreliable. Also causing issues is that in Stukeley's illustrations, the chamber entrance is not at the western end, as Ayleway claimed it was.[60]

In 1782, Edward Hasted published details of the site, perhaps drawn from information supplied by William Boys of Sandwich. His publication included an engraving of the site; Ashbee later noted that this illustration was "romanticised".[60] Hasted's suggestion was that the site had been damaged by treasure hunters.[60] Later that century, mention of Little Kit's Coty House was also made in the published work of W. H. Ireland, and John Thorpe.[60] Thorpe added the suggestion that the monument had been destroyed so that its stones could be used for dockyard paving.[60] In an 1824 issue of the Gentleman's Magazine, a note on the site was published by Edward Rudge. He included an illustration of the site.[62] Describing the site as "a Druidical monument consisting of five or six cromlechs", he added that digging beneath one of the stones had revealed human bone and armour.[62]
It is in the 1840s that several brief references to the site appeared which first called it the Countless Stones.[62] In the early 1840s, the Reverend Beale Post conducted investigations into the Medway Megaliths, writing them up in a manuscript that was left unpublished; this included Little Kit's Coty House. He disputed both Hasted and Thorpe's ideas about how the monument had been destroyed, suggesting that instead a sepulchral cavity had given way, after which the impact of the weather brought the chamber crashing down.[63] In 1871, Edwin Dunkin published a plan of the site;[64] his differed from that of Rudge, perhaps reflecting the changes that had occurred at the site in the intervening period.[62]
In 1883, both this site and Kit's Coty House were visited by the archaeologist Augustus Pitt Rivers. He communicated with the landowner, H. A. Brassey, who believed that both sites should be protected under the new Ancient Monuments Protection Act 1882.[62] In 1897, the site was declared a protected monument, two years after Kit's Coty House had.[65] Meanwhile, in 1893, the antiquarian George Payne mentioned the monument in his Collectanea Cantiana, describing it as a "fallen cromlech" and noting that there were various other megaliths scattered in the vicinity, suggesting that these were part of the monument or another like it, since destroyed.[66] In 1907, F. J. Bennett published a "Sketch Plan of the Countless Stones",[67] and in 1908 George Clinch published a photograph of it.[68] Clinch's photograph features the substantial trees located near the site which were still extant in the 1930s but were later removed.[62] In his 1924 publication dealing with Kent, the archaeologist O. G. S. Crawford, then working as the archaeological officer for the Ordnance Survey, listed Lower Kit's Coty House alongside the other Medway Megaliths, like Bennett referring to it as the Countless Stones.[69]
In 1994, a pipe trench was cut alongside the site, during which evidence of a ditch below ploughsoil and hillwash was found.[70]
References
[edit]Footnotes
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f Jessup 1970, p. 100.
- ^ Jessup 1970, p. 100; Ashbee 2000, p. 328; Philp & Dutto 2005, p. 6.
- ^ a b c d Philp & Dutto 2005, p. 6.
- ^ Hutton 1991, pp. 16–17.
- ^ Hutton 1991, p. 16; Ashbee 1999, p. 272; Hutton 2013, pp. 34–35.
- ^ Holgate 1981, pp. 230–231.
- ^ Hutton 2013, p. 37.
- ^ Barclay et al. 2006, p. 20.
- ^ Barclay et al. 2006, pp. 25–26.
- ^ Champion 2007, pp. 73–74; Hutton 2013, p. 33.
- ^ Hutton 1991, p. 19; Hutton 2013, p. 37.
- ^ Hutton 1991, p. 19; Hutton 2013, p. 40.
- ^ Hutton 1991, p. 19.
- ^ a b Malone 2001, p. 103.
- ^ Hutton 2013, p. 40.
- ^ Malone 2001, pp. 103–104; Hutton 2013, p. 41.
- ^ a b Hutton 2013, p. 41.
- ^ Holgate 1981, p. 225; Champion 2007, p. 78.
- ^ Champion 2007, p. 76.
- ^ Wysocki et al. 2013, p. 1.
- ^ Garwood 2012, p. 1.
- ^ Holgate 1981, p. 221.
- ^ Philp & Dutto 2005, p. 1.
- ^ a b Ashbee 1999, p. 269.
- ^ Ashbee 1993, pp. 60–61; Champion 2007, p. 78; Wysocki et al. 2013, p. 1.
- ^ Ashbee 2005, p. 101; Champion 2007, pp. 76–77.
- ^ Ashbee 2005, p. 101; Champion 2007, p. 78.
- ^ a b Holgate 1981, p. 223.
- ^ Holgate 1981, pp. 223, 225.
- ^ a b c d e f g Champion 2007, p. 78.
- ^ Killick 2010, p. 339.
- ^ a b Ashbee 1993, p. 58; Ashbee 2000, pp. 325–326; Champion 2007, p. 78.
- ^ Holgate 1981, p. 225; Wysocki et al. 2013, p. 3.
- ^ Wysocki et al. 2013, p. 3.
- ^ Ashbee 1993, p. 60.
- ^ a b Holgate 1981, p. 227.
- ^ Piggott 1935, p. 122.
- ^ Daniel 1950, p. 161.
- ^ Evans 1950, pp. 77−80.
- ^ Jessup 1970, p. 111.
- ^ Ashbee 1999, p. 271.
- ^ Ashbee 1993, p. 57.
- ^ a b c Ashbee 2000, p. 328.
- ^ Ashbee 2005, pp. 110–111.
- ^ Ashbee 1993, p. 82; Ashbee 2000, p. 328.
- ^ Burl 1981, p. 61; Malone 2001, p. 103.
- ^ Burl 1981, p. 61.
- ^ Malone 2001, pp. 106–107.
- ^ Malone 2001, p. 107.
- ^ Hutton 2013, pp. 42–43.
- ^ Hutton 2013, p. 43.
- ^ Hutton 2013, p. 39.
- ^ Hutton 2013, pp. 39–40.
- ^ Burl 1981, p. 63.
- ^ Grinsell 1976, p. 124; Doel & Doel 2003, p. 104.
- ^ a b Grinsell 1976, p. 123.
- ^ a b Doyle White 2016, p. 351.
- ^ a b c Ashbee 1993, p. 79.
- ^ a b Ashbee 1993, pp. 79–80.
- ^ a b c d e f Ashbee 1993, p. 80.
- ^ Ashbee 2005, p. 21.
- ^ a b c d e f Ashbee 1993, p. 81.
- ^ Evans 1949, p. 134.
- ^ Dunkin 1871, p. 74; Ashbee 1993, p. 81.
- ^ Ashbee 1993, p. 81; Ashbee 2005, p. 193.
- ^ Payne 1893, pp. 126–127.
- ^ Bennett 1907, p. 48; Ashbee 1993, pp. 81–82.
- ^ Clinch 1908, p. 319; Ashbee 1993, p. 81.
- ^ Ashbee 1993, p. 82.
- ^ Ashbee 2005, p. 107.
Bibliography
[edit]- Ashbee, Paul (1993). "The Medway Megaliths in Perspective" (PDF). Archaeologia Cantiana. 111. Kent Archaeological Society: 57–112.
- Ashbee, Paul (1993b). "William Stukeley, the Kit's Coty House and his Coves: A Note". Archaeologia Cantiana. 112. Kent Archaeological Society: 17–24.
- Ashbee, Paul (1999). "The Medway Megaliths in a European Context" (PDF). Archaeologia Cantiana. 119. Kent Archaeological Society: 269–284.
- Ashbee, Paul (2000). "The Medway's Megalithic Long Barrows" (PDF). Archaeologia Cantiana. 120. Kent Archaeological Society: 319–345.
- Ashbee, Paul (2005). Kent in Prehistoric Times. Stroud: Tempus. ISBN 978-0752431369.
- Barclay, Alistair; Fitzpatrick, Andrew P.; Hayden, Chris; Stafford, Elizabeth (2006). The Prehistoric Landscape at White Horse Stone, Aylesford, Kent (Report). Oxford: Oxford Wessex Archaeology Joint Venture (London and Continental Railways).
- Bennett, F. J. (1907). Ightham: The Story of a Kentish Village and its Surroundings. London.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Burl, Aubrey (1981). Rites of the Gods. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 978-0460043137.
- Champion, Timothy (2007). "Prehistoric Kent". In John H. Williams (ed.). The Archaeology of Kent to AD 800. Woodbridge: Boydell Press and Kent County Council. pp. 67–133. ISBN 9780851155807.
- Clinch, G. (1908). "Kentish Megalithic Structures". Victoria County History: Kent Volume I. pp. 318–320.
- Daniel, Glynn E. (1950). The Prehistoric Chamber Tombs of England and Wales. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Doel, Fran; Doel, Geoff (2003). Folklore of Kent. Stroud: Tempus. ISBN 978-0-7524-2628-0.
- Doyle White, Ethan (2016). "Old Stones, New Rites: Contemporary Pagan Interactions with the Medway Megaliths". Material Religion. 12 (3): 346–372. doi:10.1080/17432200.2016.1192152. S2CID 218836456.
- Dunkin, E. H. W. (1871). "On the Megalithic Remains in Mid-Kent". The Reliquary. 12: 67–80.
- Evans, John H. (1946). "Notes on the Folklore and Legends Associated with the Kentish Megaliths". Folklore. 57 (1). The Folklore Society: 36–43. doi:10.1080/0015587x.1946.9717805. JSTOR 1257001.
- Evans, John H. (1949). "A Disciple of the Druids; the Beale Post Mss" (PDF). Archaeologia Cantiana. 62. Kent Archaeological Society: 130–139.
- Evans, John H. (1950). "Kentish Megalith Types" (PDF). Archaeologia Cantiana. 63. Kent Archaeological Society: 63–81.
- Garwood, P. (2012). "The Medway Valley Prehistoric Landscapes Project". PAST: The Newsletter of the Prehistoric Society. 72. The Prehistoric Society: 1–3.
- Grinsell, Leslie V. (1976). Folklore of Prehistoric Sites in Britain. London: David & Charles. ISBN 978-0-7153-7241-8.
- Holgate, Robin (1981). "The Medway Megaliths and Neolithic Kent" (PDF). Archaeologia Cantiana. 97. Kent Archaeological Society: 221–234.
- Hutton, Ronald (1991). The Pagan Religions of the Ancient British Isles: Their Nature and Legacy. Oxford, U.K. and Cambridge, U.S.: Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-631-17288-8.
- Hutton, Ronald (2013). Pagan Britain. New Haven and London: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-197716.
- Jessup, Ronald F. (1970). South-East England. London: Thames and Hudson. ISBN 9780500020685.
- Killick, Sian (2010). "Neolithic Landscape and Experience: The Medway Megaliths" (PDF). Archaeologia Cantiana. Vol. 130. Kent Archaeological Society. pp. 339–349.
- Lewis, A.L. (1878). "On a Rude Stone Monument in Kent". The Journal of the Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland. 7: 140–142. doi:10.2307/2841379. JSTOR 2841379.
- Malone, Caroline (2001). Neolithic Britain and Ireland. Stroud, Gloucestershire: Tempus. ISBN 978-0-7524-1442-3.
- Menefee, S.P. (1975). "The 'Countless Stones': A Final Reckoning". Folklore. 86 (3–4). The Folklore Society: 146–166. doi:10.1080/0015587x.1975.9716017. JSTOR 1260230.
- Payne, George (1893). Collectanea Cantiana: Or, Archæological Researches in the Neighbourhood of Sittingbourne, and Otherparts of Kent. London: Mitchell and Hughes.
- Philp, Brian; Dutto, Mike (2005). The Medway Megaliths (third ed.). Kent: Kent Archaeological Trust.
- Piggott, Stuart (1935). "A Note on the Relative Chronology of the English Long Barrows". Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society. 1. The Prehistoric Society: 115–126. doi:10.1017/s0079497x00022246. S2CID 130433541.
- Wright (1844). "Proceedings of the Committee". The Archaeological Journal. 1: 262–264.
- Wysocki, Michael; Griffiths, Seren; Hedges, Robert; Bayliss, Alex; Higham, Tom; Fernandez-Jalvo, Yolanda; Whittle, Alasdair (2013). "Dates, Diet and Dismemberment: Evidence from the Coldrum Megalithic Monument, Kent". Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society. 79. Prehistoric Society: 1–30. doi:10.1017/ppr.2013.10.

